
Extended exposure to the sun's UV rays has been linked to significant eye problems, including cataracts, macular degeneration, pingueculae, pterygia and photokeratitis
Protecting your eyes from UV
To protect your eyes from harmful solar radiation, your should wear sunglasses that block 100 percent UV whenever you are outdoors in daylight. Your eyes need protection even on cloudy days because the sun's damaging UV rays can penetrate cloud cover.Sunglass frames with a close-fitting wraparound
What is UV?
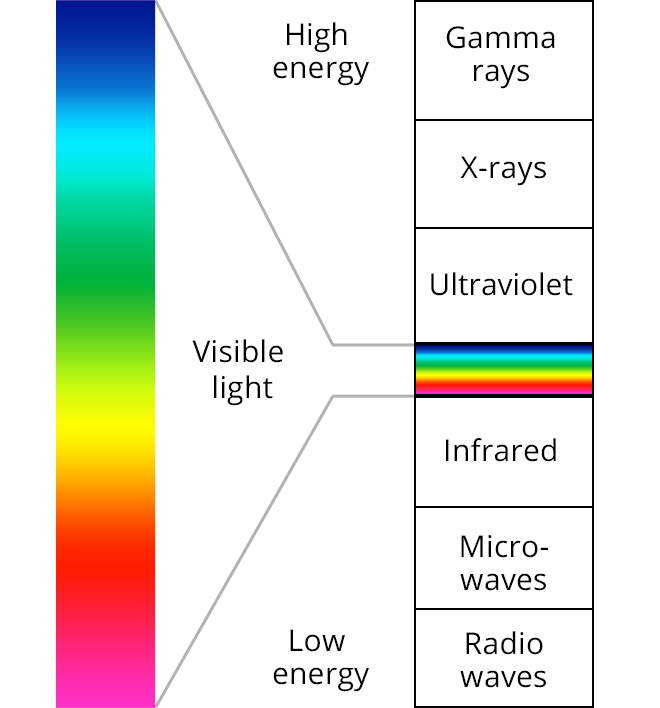
There are three categories of UV radiation:
UVC
These are the highest energy UV rays and potentially could be the most harmful to your eyes and skin. Fortunately, the atmosphere's ozone layer blocks virtually all UVC rays.But this also means depletion of the ozone layer potentially could allow high-energy UVC rays to reach the Earth's surface and cause serious UV-related health problems.
UVC rays have wavelengths that range from 100 to 280 nanometers (nm).
UVB
UVB rays have slightly longer wavelengths (280-315 nm) and lower energy than UVC rays. These rays are filtered partially by the ozone layer, but some still reach the Earth's surface.In low doses, UVB radiation stimulates the production of melanin
Overexposure to the sun's UVB radiation also is associated with a number of eye problems, including pinguecula, pterygium.
Because the cornea appears to absorb 100 percent of UVB rays, this type of UV radiation is unlikely to cause cataracts and macular degeneration, which instead is linked to UVA exposure (see below).
UVA
UVA rays are closer to visible light rays and have lower energy than UVB and UVC rays. But UVA rays can pass through the cornea and reach the lens and retina inside the eye.Overexposure to UVA radiation has been linked to the development of certain types of cataracts, and research suggests UVA rays may play a role in development of macular degeneration.
UV risk factors

- Geographic location UV exposure is greater in tropical areas near the earth's equator. The farther you are from the equator, the smaller your risk.
- Altitude UV exposure is greater at higher altitudes.
- Time of day UV exposure is greater when the sun is high in the sky, typically from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m.
- Setting UV exposure generally is greater in wide open spaces, especially when highly reflective surfaces are present, like snow and sand. In fact, UV exposure can nearly double when UV rays are reflected from the snow. UV exposure is less likely in urban settings, where tall buildings shade the streets.
- Medications Certain medications, such as tetracycline, sulfa drugs, birth control pills, diuretics and tranquilizers, can increase your body's sensitivity to UV radiation.
Measuring Ultraviolet Rays
In the United States, the risk for UV exposure is measured using the UV Index.Developed by the NWS and EPA, the UV Index predicts each day's ultraviolet radiation levels on a simple 1 to 11+ scale.
In addition to publishing the UV Index daily, the EPA also issues a UV Alert when the level of solar UV radiation that day is expected to be unusually high.
| UV Index | Risk Level | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| 2 or less | Low | 1. Wear sunglasses. 2. If you burn easily, use sunscreen with an SPF* of 15+. |
| 3 - 5 | Moderate | 1. Wear sunglasses. 2. Cover up and use sunscreen. 3. Stay in the shade near midday, when the sun is strongest. |
| 6 - 7 | High | 1. Wear a hat and sunglasses. 2. Cover up and use sunscreen. 3. Reduce time in the sun between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. |
| 8 - 10 | Very high | 1. Wear a hat and sunglasses. 2. Cover up and use sunscreen. 3. Minimize sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. |
| 11+ | Extreme | 1. Wear a hat and sunglasses. 2. Apply sunscreen (SPF 15+) liberally every two hours. 3. Try to avoid sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. |
| *SPF = sun protection factor Information based on U.S. Environmental Protection Agency standards. | ||
Children need UV protection, too
The risk of damage to our eyes and skin from solar UV radiation is cumulative — meaning the danger continues to grow the more time you spend in sunlight throughout your lifetime.With this in mind, it's especially important for kids to protect their eyes from the sun. Children generally spend much more time outdoors than adults.
In fact, some experts say that because children tend to spend significantly more time outdoors than most adults, up to half of a person's lifetime exposure to UV radiation can occur by age 18.
Also, children are more susceptible to eye damage from UV rays because the lens inside a child's eye is clearer than an adult lens, enabling more UV to penetrate deep into the eye.

Many misconceptions exist about sun protection for your eyes. Keep these tips in mind:
- Not all sunglasses block 100 percent of UV rays. If you're unsure about the level of UV protection your sunglasses provide, take them to your eye doctor for an evaluation. Many eye care professionals have instruments that can measure the amount of UV radiation your lenses block.
- Remember to wear sunglasses even when you're in the shade. Although shade reduces your UV and HEV exposure to some degree, your eyes still will be exposed to UV rays reflected from buildings, roadways and other surfaces.
- Sunglasses also are important in winter, because fresh snow can reflect 80 percent of UV rays, nearly doubling your overall exposure to solar UV radiation. If you ski or snowboard, choosing the right lenses is essential for adequate UV protection on the slopes.
- Even if your contact lenses block UV rays, you still need sunglasses. UV-blocking contacts shield only the part of your eye under the lens. UV rays still can damage your eyelids and other tissues not covered by the lens. Wearing sunglasses protects these delicate tissues and the skin around your eyes from UV damage.
- If you have dark skin and eyes, you still need to wear sunglasses. Although dark skin color may give you a lower risk of skin cancer from UV radiation, your risk of eye damage from UV rays is the same as that of someone with fair skin.

0 Comments